Architecture
Alauda Streaming Service for Kafka leverages Kafka's distributed architecture to provide a proven high-availability solution, meeting enterprise requirements for high-throughput, reliable, and elastically scalable message queuing systems.
TOC
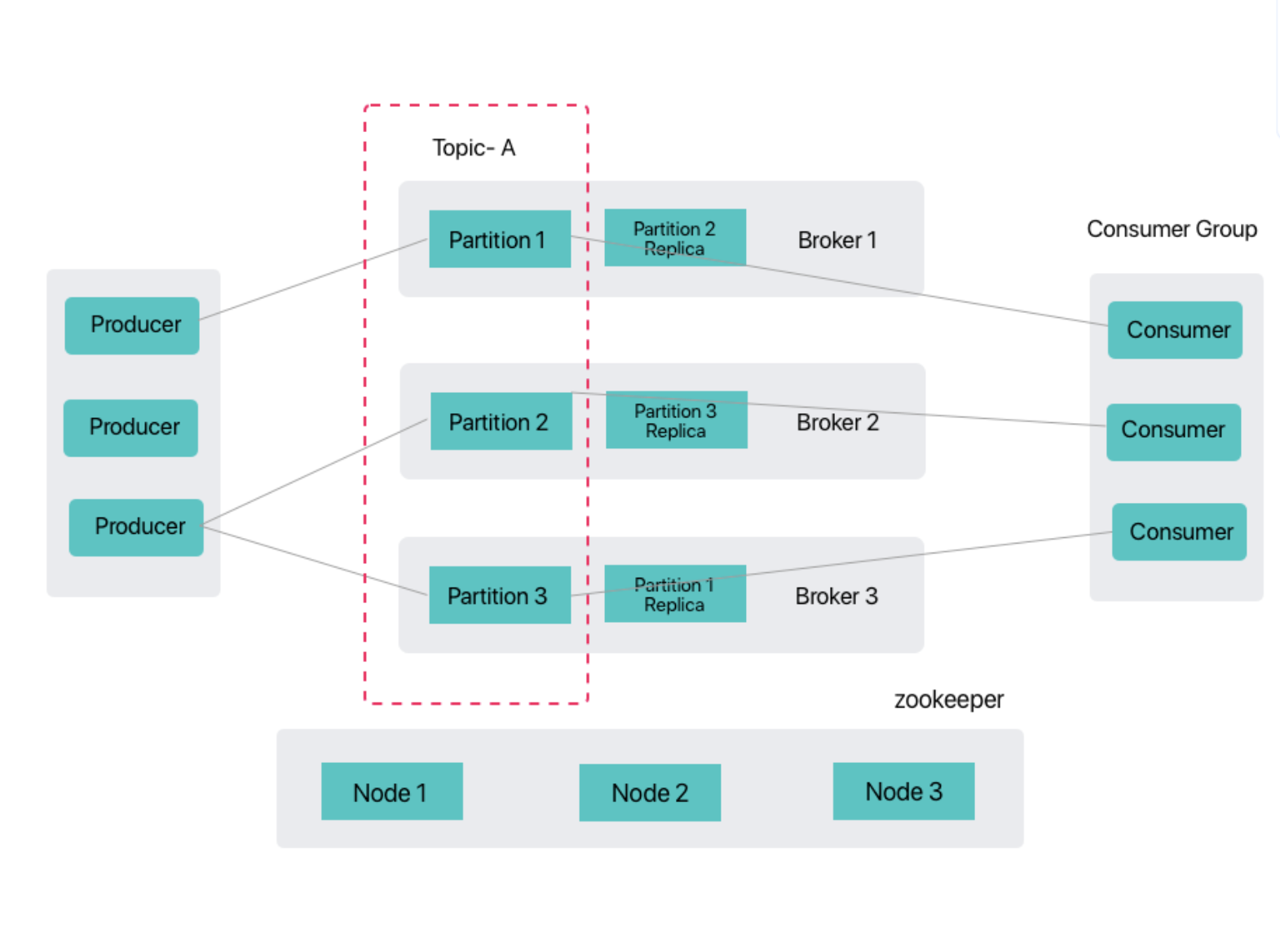
ZooKeeper Coordination Mode
The ZooKeeper coordination mode is the traditional distributed coordination implementation for Kafka, utilizing a ZooKeeper cluster to manage Kafka cluster metadata, Broker registration, and controller election, among other core functionalities. This mode has the following characteristics:
- Mature and Stable: Verified in large-scale production environments, it has extremely high reliability.
- Separation of Concerns: ZooKeeper focuses on cluster coordination, while Kafka brokers concentrate on message processing.
- Automatic Failover: Controller automatic election achieved via ZooKeeper's watcher mechanism.
- Metadata Management: Stores key metadata such as topic partition information and consumer offsets.
- Expansion Dependency: Requires additional maintenance of a ZooKeeper cluster, introducing operational complexity.
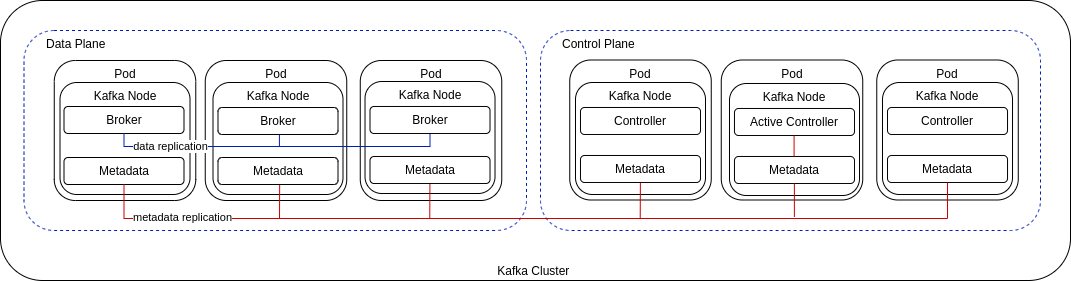
KRaft Mode
KRaft mode is Kafka's next-generation metadata management system, which replaces ZooKeeper with Kafka's native Raft-based consensus protocol. This mode offers the following characteristics:
- Simplified Architecture: Eliminates the external ZooKeeper dependency, reducing operational complexity.
- Enhanced Scalability: Supports significantly more partitions (up to millions, compared to hundreds of thousands in ZooKeeper mode).
- Faster Controller Failover: Achieves sub-second failover, a substantial improvement over ZooKeeper's multi-second failover latency.
- Stronger Consistency: Ensures linearizable metadata operations, providing stronger consistency guarantees than the eventual consistency of ZooKeeper-based metadata.
- Flexible Deployment: Supports both combined mode (unified processes acting as both brokers and controllers, suitable for small clusters) and dedicated mode (separate controller and broker processes, ideal for large-scale deployments).